PyMLpipe
PyMLpipe is a Python library for ease Machine Learning Model monitoring and Deployment.
- Simple
- Intuative
- Easy to use
Please Find the Full documentation here!
Installation
Use the package manager pip to install PyMLpipe.
pip install pymlpipe
or
pip3 install pymlpipe
Frame Work Supports
- [X] Scikit-Learn
- [X] XGBoost
- [X] LightGBM
- [X] Pytorch
- [ ] Tensorflow
- [ ] Keras
Tutorial (Scikit-Learn|XGBoost|LightGBM)
- Load the python package
from pymlpipe.tabular import PyMLPipe
- Initiate the
PyMLPipeclass
mlp=PyMLPipe()
- Set an Experiment Name
[Optional]-Default experiment name is'0'
mlp.set_experiment("IrisDataV2")
- Set a version
[Optional]-Default there is no version
mlp.set_version(0.1)
- Initiate the context manager - This is create a unique ID for each model run.
- when
.run()is used - Automatic unique ID is generated - you can also provide
runidargument in the.run()this will the use the givenrunidfor next storing.
- when
with mlp.run():
Or
with mlp.run(runid='mlopstest'):
- Set a Tag
[Optional]by usingset_tag()-Default there is no tags
mlp.set_tag('tag')
Or
- Set multiple Tags
[Optional]by usingset_tags()-Default there is no tags
mlp.set_tags(["Classification","test run","logisticRegression"])
- Set Metrics values
[Optional]by usinglog_matric(metric_name,metric_value)-Default there is no metrics This will help in comparing performance of different models and model versions
mlp.log_metric("Accuracy", accuracy_score(testy,predictions))
mlp.log_metric("Accuracy", .92)
- Set multiple Metrics values
[Optional]by usinglog_matrics({metric_name:metric_value})-Default there is no metrics
mlp.log_metrics(
{
"Accuracy": accuracy_score(testy,predictions),
"Precision": precision_score(testy,predictions,average='macro'),
"Recall", recall_score(testy,predictions,average='macro'),
}
)
mlp.log_metrics(
{
"Accuracy": .92,
"Precision": .87,
"Recall", .98,
}
)
- Save an artifact
[Optional]- You can save training/testing/validation/dev/prod data for monitoring and comparison- This will also help in generating
DATA SCHEMA register_artifact()-takes 3 arguments- name of artifact
- Pandas Dataframe
- type of artifact -
[training, testing, validation, dev, prod]
- You can also use
register_artifact_with_path()- This will save the artifact from the disk.- Path for the file
- type of artifact -
[training, testing, validation, dev, prod]
- This will also help in generating
mlp.register_artifact("train.csv", trainx)
mlp.register_artifact("train.csv", trainx)
- Register Model
[Optional]- You can register the model. This will help in Quick deployment
mlp.scikit_learn.register_model("logistic regression", model)
Quick Start (Scikit-Learn|XGBoost|LightGBM)
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,precision_score,recall_score,f1_score
#import PyMLPipe from tabular
from pymlpipe.tabular import PyMLPipe
# Initiate the class
mlp=PyMLPipe()
# Set experiment name
mlp.set_experiment("IrisDataV2")
# Set Version name
mlp.set_version(0.2)
iris_data=load_iris()
data=iris_data["data"]
target=iris_data["target"]
df=pd.DataFrame(data,columns=iris_data["feature_names"])
trainx,testx,trainy,testy=train_test_split(df,target)
# to start monitering use mlp.run()
with mlp.run():
# set tags
mlp.set_tags(["Classification","test run","logisticRegression"])
model=LogisticRegression()
model.fit(trainx, trainy)
predictions=model.predict(testx)
# log performace metrics
mlp.log_metric("Accuracy", accuracy_score(testy,predictions))
mlp.log_metric("Precision", precision_score(testy,predictions,average='macro'))
mlp.log_metric("Recall", recall_score(testy,predictions,average='macro'))
mlp.log_metric("F1", f1_score(testy,predictions,average='macro'))
# Save train data and test data
mlp.register_artifact("train", trainx)
mlp.register_artifact("test", testx,artifact_type="testing")
# Save the model
mlp.scikit_learn.register_model("logistic regression", model)
Launch UI
To start the UI
pymlpipeui
or
from pymlpipe.pymlpipeUI import start_ui
start_ui(host='0.0.0.0', port=8085)
Sample UI
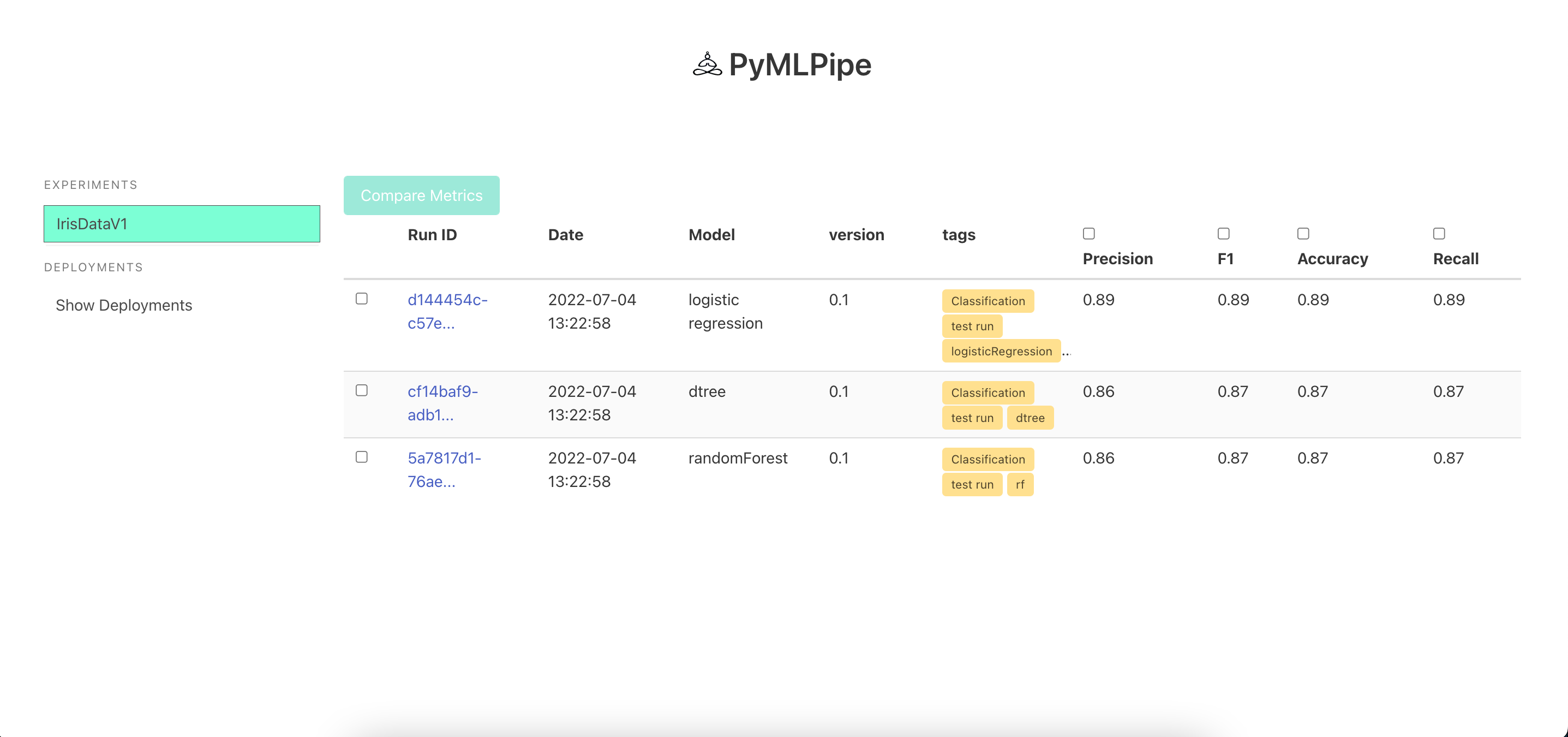
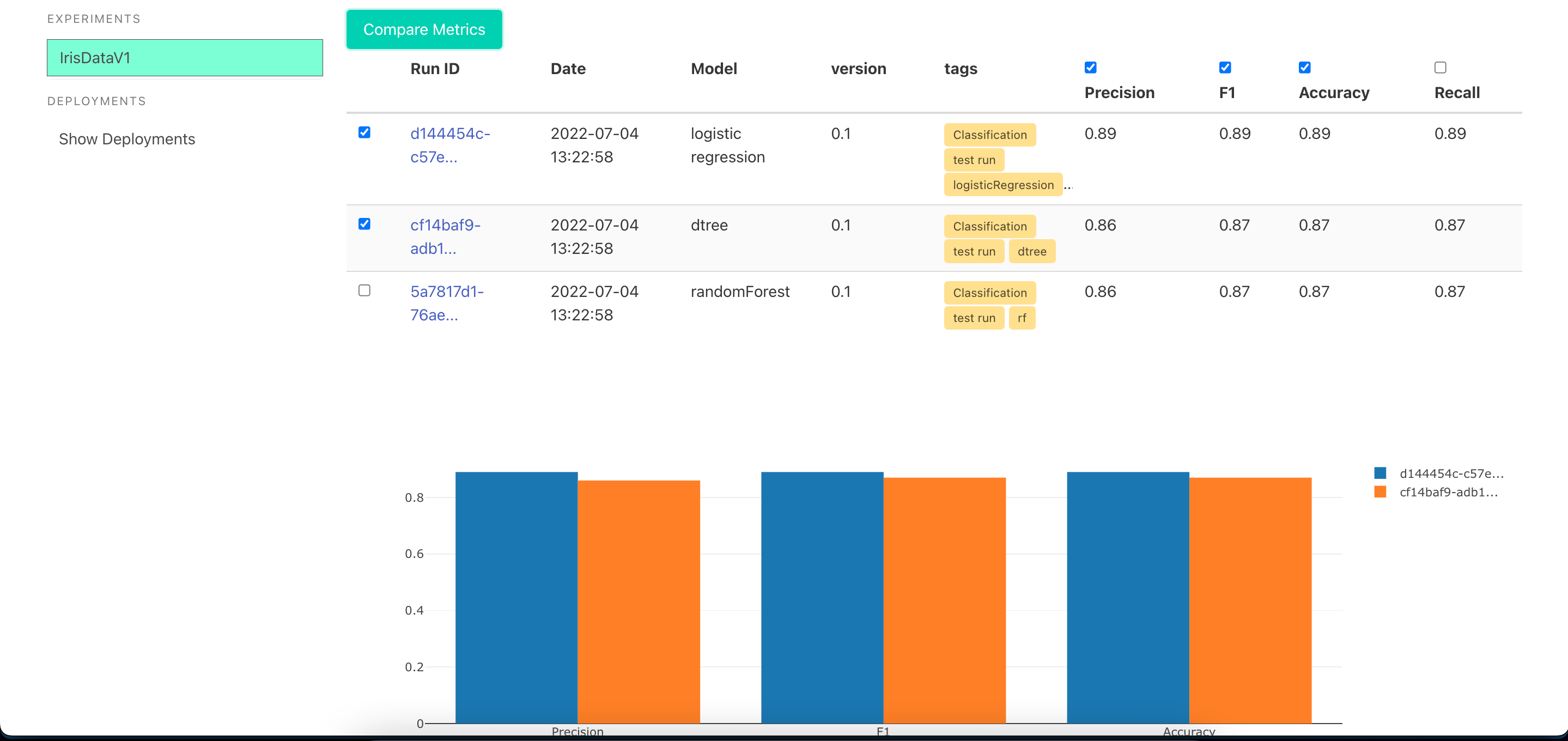
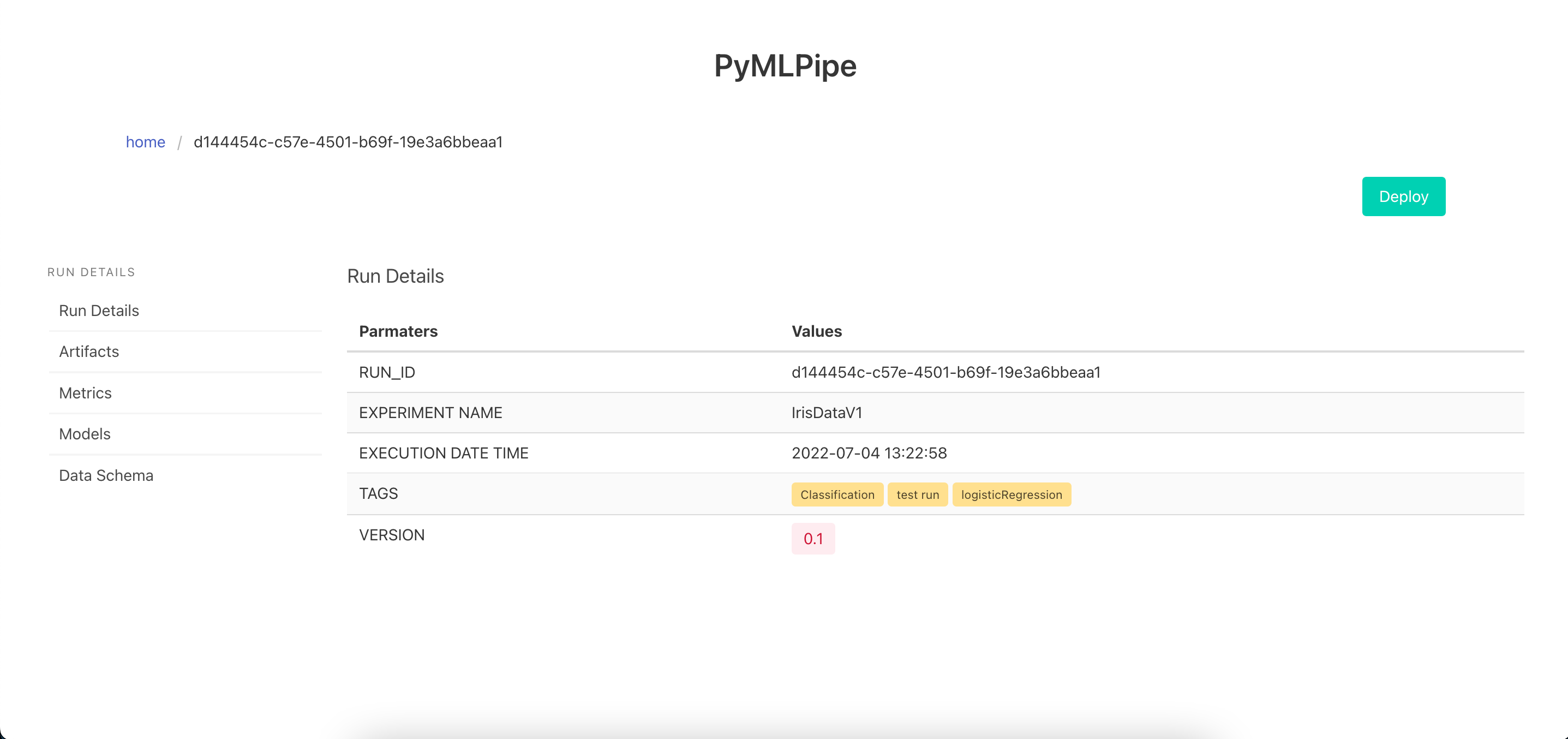
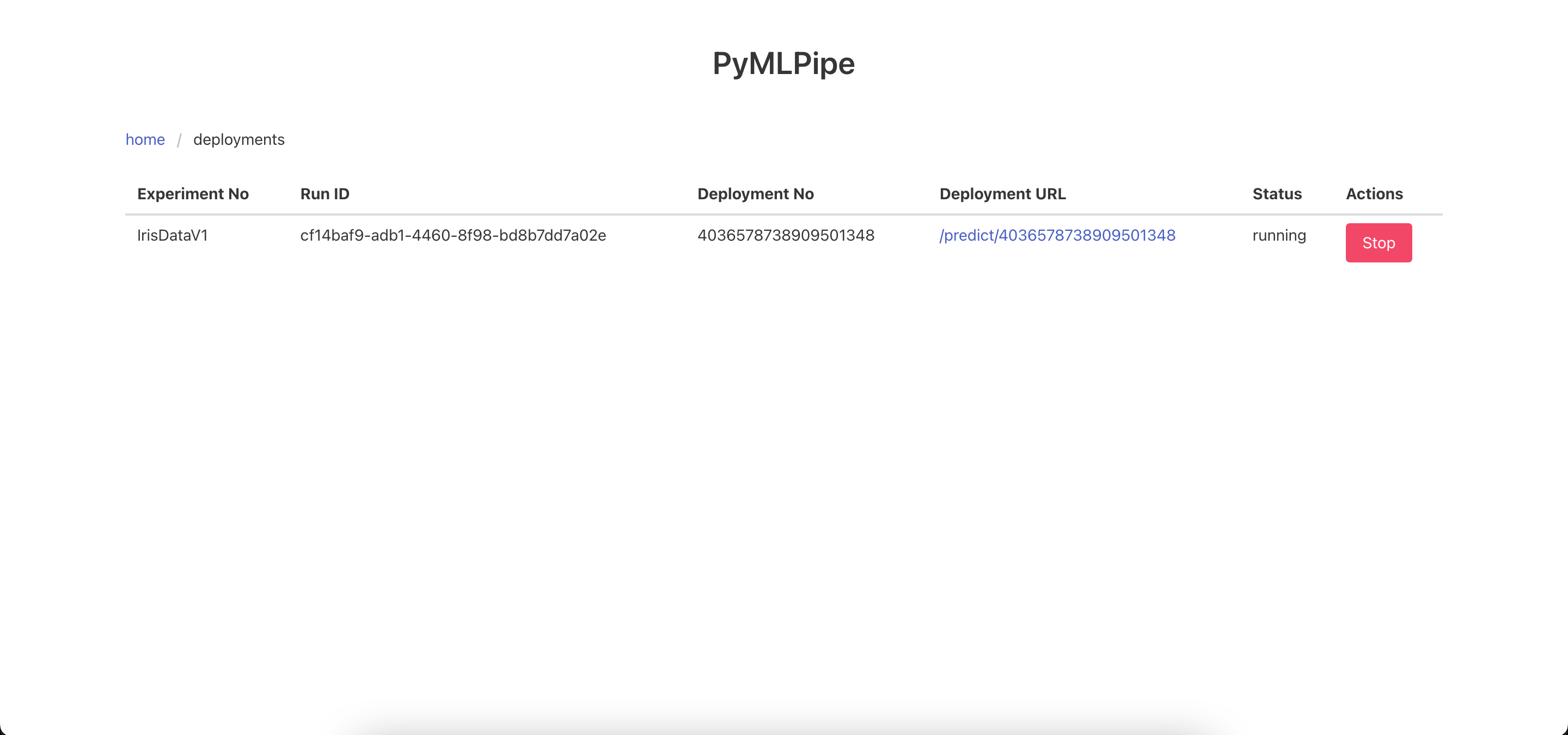
One Click Deployment -click the deploy button to deploy the model and get a endpoint
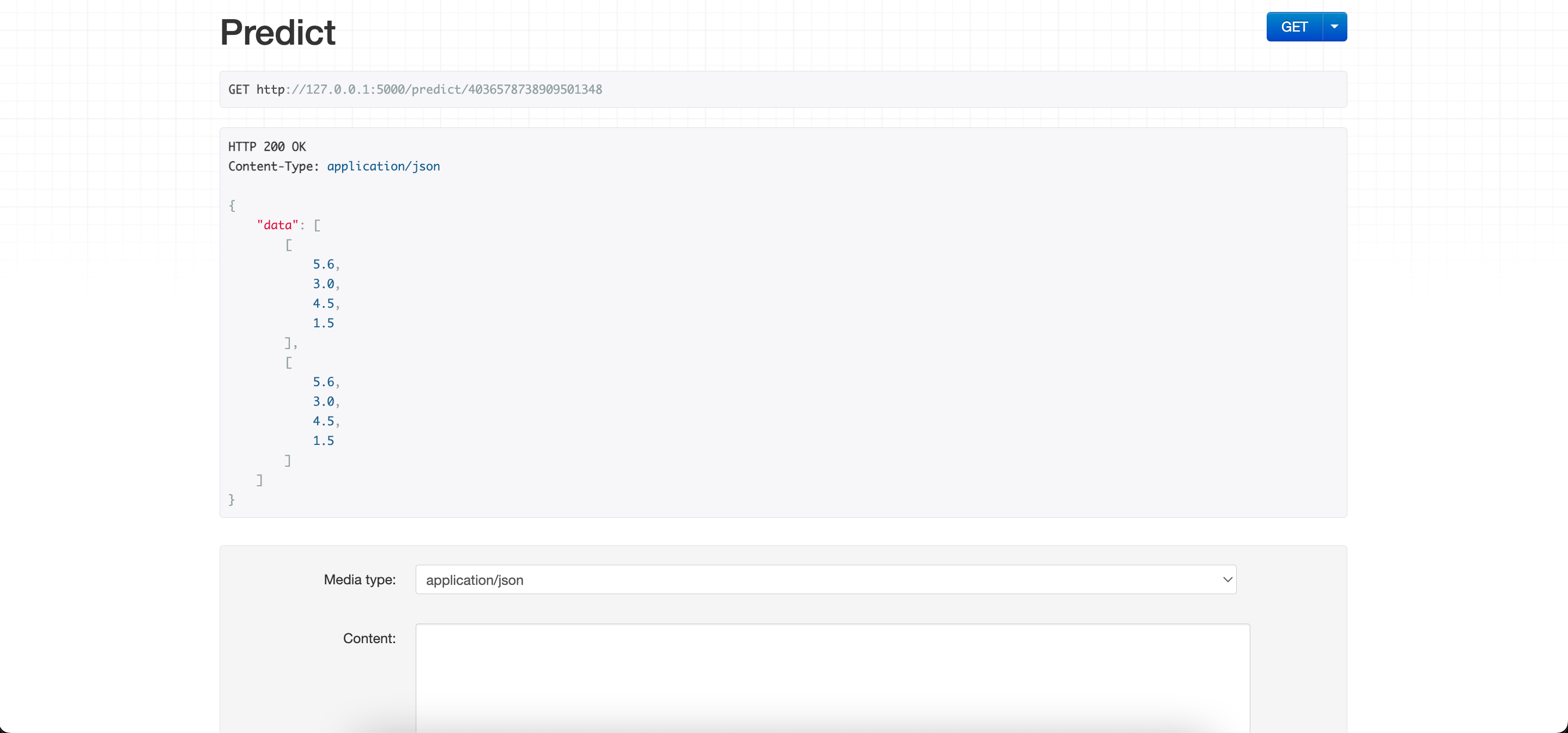
Send the data to the Prediction end point in the format
- Each list is a row of data
{
"data":[
[
5.6,
3.0,
4.5,
1.5
],
[
5.6,
3.0,
4.5,
1.5
]
]
}
Tutorial (Pytorch)
The previous methods can be used as it is. New methods are shown below
- Log continious Metrics
.log_metrics_continious(dict)--> dict of metrics\ - logs the metrics in a continious manner for each epoch
mlp.log_metrics_continious({
"accuracy": .9,
"precision": .8,
"recall": .7
})
- To register a pytorch model use
.pytorch.register_model(modelname, modelobject)- this will Save the model in a .pt file as a
torch.jitformat for serveing and prediction
- this will Save the model in a .pt file as a
mlp.pytorch.register_model("pytorch_example1", model)
-
To register a pytorch model use
.pytorch.register_model_with_runtime(modelname, modelobject, train_data_sample)train_data_sample- is a sample of input data. it can be random numbers but needs tensor dimension- This method is
preferredas infuture releasesthis models can be then converted to other formats as well ex: "onnx", "hd5"
mlp.pytorch.register_model_with_runtime("pytorch_example1", model, train_x)
Quick Start (Pytorch)
import torch
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,f1_score
from pymlpipe.tabular import PyMLPipe
df=pd.read_csv("train.csv")
encoders=["area_code","state","international_plan","voice_mail_plan","churn"]
for i in encoders:
le=LabelEncoder()
df[i]=le.fit_transform(df[i])
trainy=df["churn"]
trainx=df[['state', 'account_length', 'area_code', 'international_plan',
'voice_mail_plan', 'number_vmail_messages', 'total_day_minutes',
'total_day_calls', 'total_day_charge', 'total_eve_minutes',
'total_eve_calls', 'total_eve_charge', 'total_night_minutes',
'total_night_calls', 'total_night_charge', 'total_intl_minutes',
'total_intl_calls', 'total_intl_charge',
'number_customer_service_calls']]
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,col_size):
super().__init__()
# using sequencial
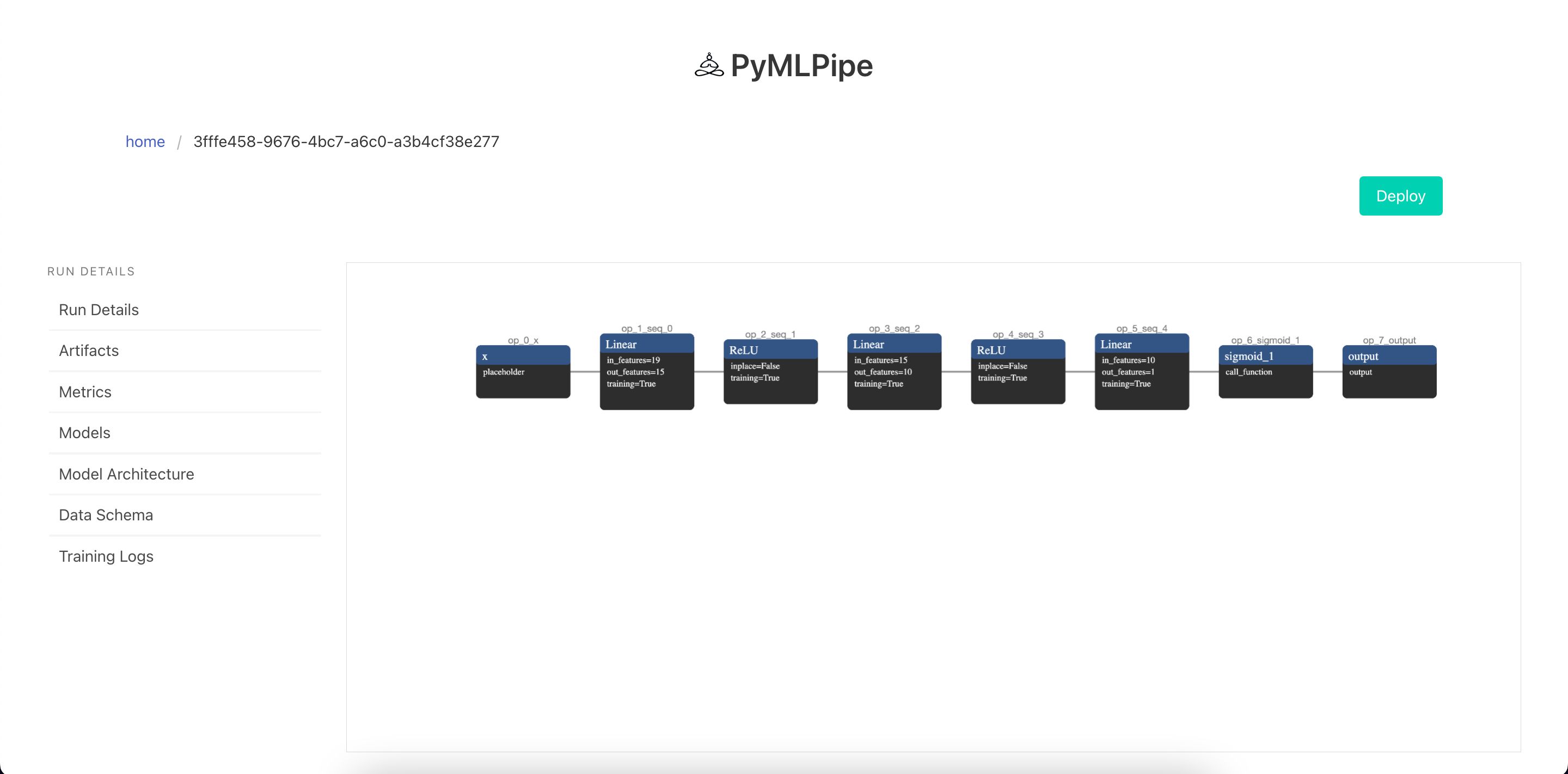
self.seq=torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(col_size,15),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(15,10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10,1)
)
#using torch layers
'''
self.linear_layer_1=torch.nn.Linear(col_size,15)
self.relu_1=torch.nn.ReLU()
self.linear_layer_2=torch.nn.Linear(15,10)
self.relu_2=torch.nn.ReLU()
self.linear_layer_3=torch.nn.Linear(10,1)
'''
def forward(self,x):
out=self.seq(x)
'''
out=self.relu_1(self.linear_layer_1(x))
out=self.relu_12self.linear_layer_3(out))
out=self.linear_layer_3(out)
'''
return torch.sigmoid(out)
model=Model(len(trainx.columns))
train_x,test_x,train_y,test_y=train_test_split(trainx,trainy)
train_x=torch.from_numpy(train_x.values)
train_x=train_x.type(torch.FloatTensor)
train_y=torch.from_numpy(train_y.values)
train_y=train_y.type(torch.FloatTensor)
test_x=torch.from_numpy(test_x.values)
test_x=test_x.type(torch.FloatTensor)
test_y=torch.from_numpy(test_y.values)
test_y=test_y.type(torch.FloatTensor)
optimizer=torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.001)
criterion=torch.nn.BCELoss()
def validate(model,testx,testy):
prediction=model(testx)
prediction=torch.where(prediction>.5,1,0)
accu=accuracy_score(prediction.detach().numpy(),test_y.unsqueeze(1).detach().numpy())
f1=f1_score(prediction.detach().numpy(),test_y.unsqueeze(1).detach().numpy())
return {"accuracy":accu,"f1":f1}
epochs=100
batch_size=1000
mlp=PyMLPipe()
mlp.set_experiment("Pytorch")
mlp.set_version(0.2)
with mlp.run():
mlp.register_artifact("churndata.csv",df)
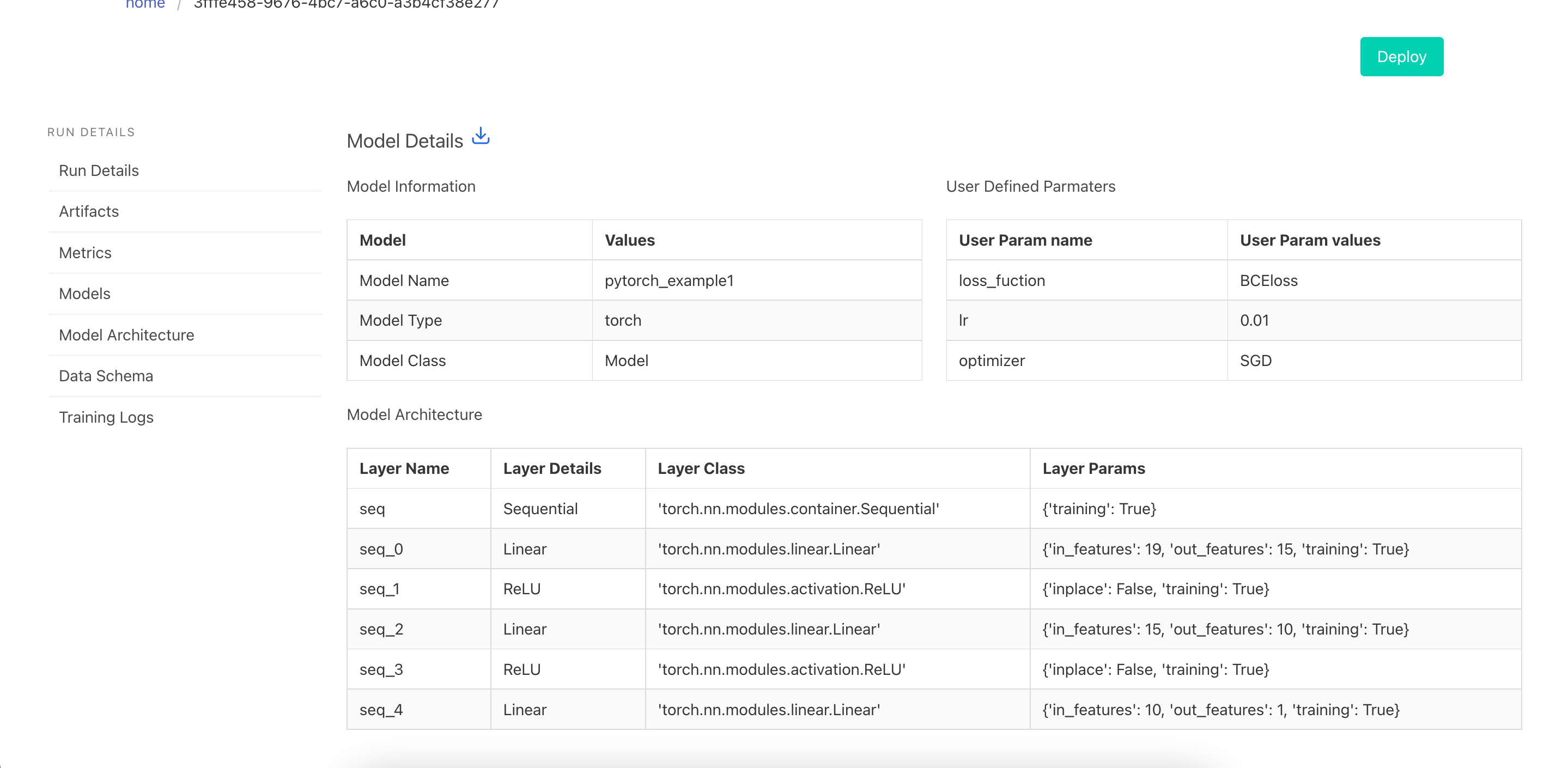
mlp.log_params({
"lr":0.01,
"optimizer":"SGD",
"loss_fuction":"BCEloss"
})
for epoch in range(epochs):
loss_batch=0
for batch in range(1000,5000,1000):
optimizer.zero_grad()
train_data=train_x[batch-1000:batch]
output=model(train_data)
loss=criterion(output,train_y[batch-1000:batch].unsqueeze(1))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss_batch+=loss.item()
metrics=validate(model,test_x,test_y)
metrics["loss"]=loss_batch
metrics["epoch"]=epoch
mlp.log_metrics_continious(metrics)
mlp.pytorch.register_model("pytorch_example1", model)
UI for Pytorch Models
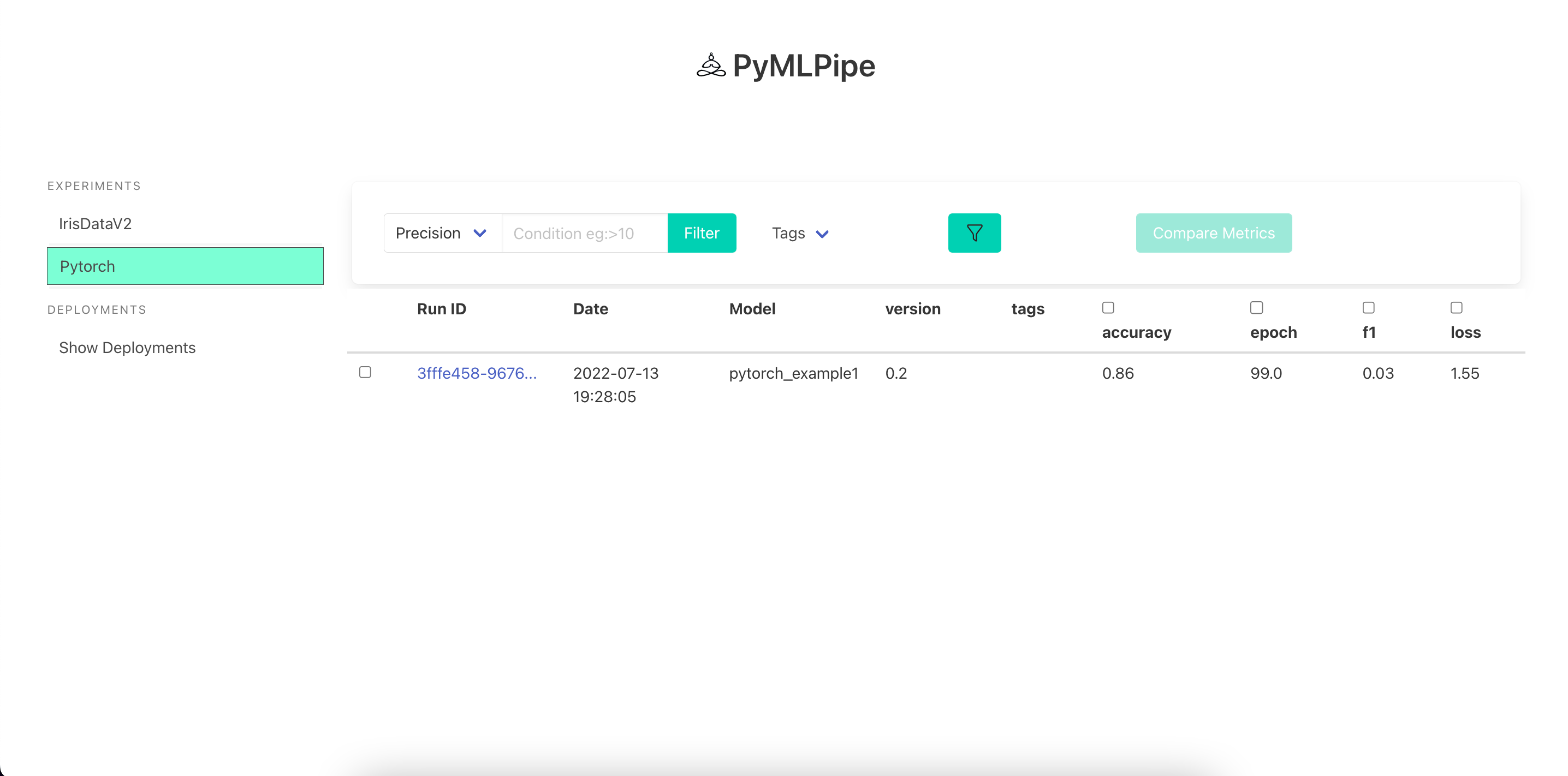
Visualize the Model details
Visualize the Model Architecture
View Training Logs
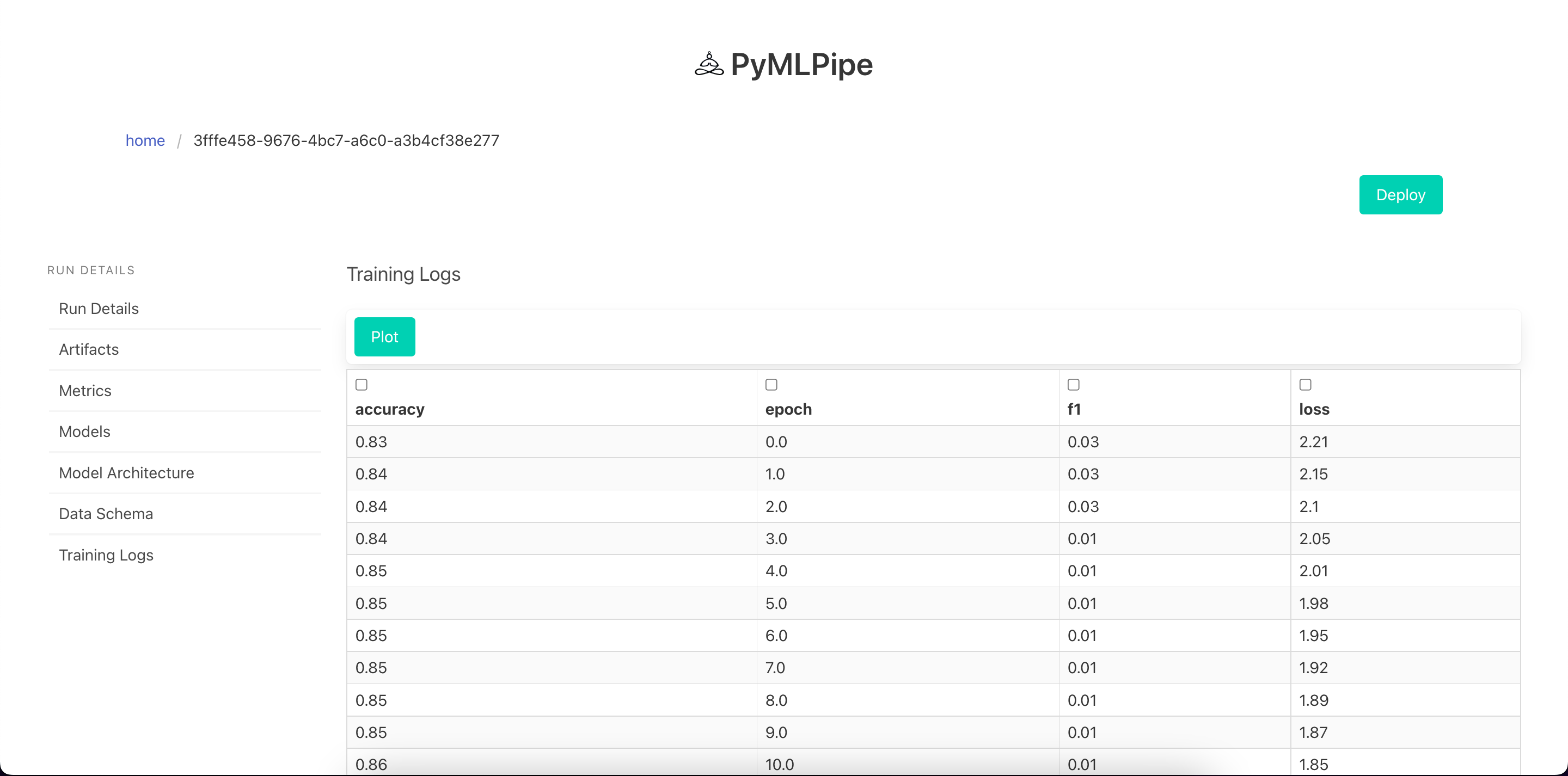
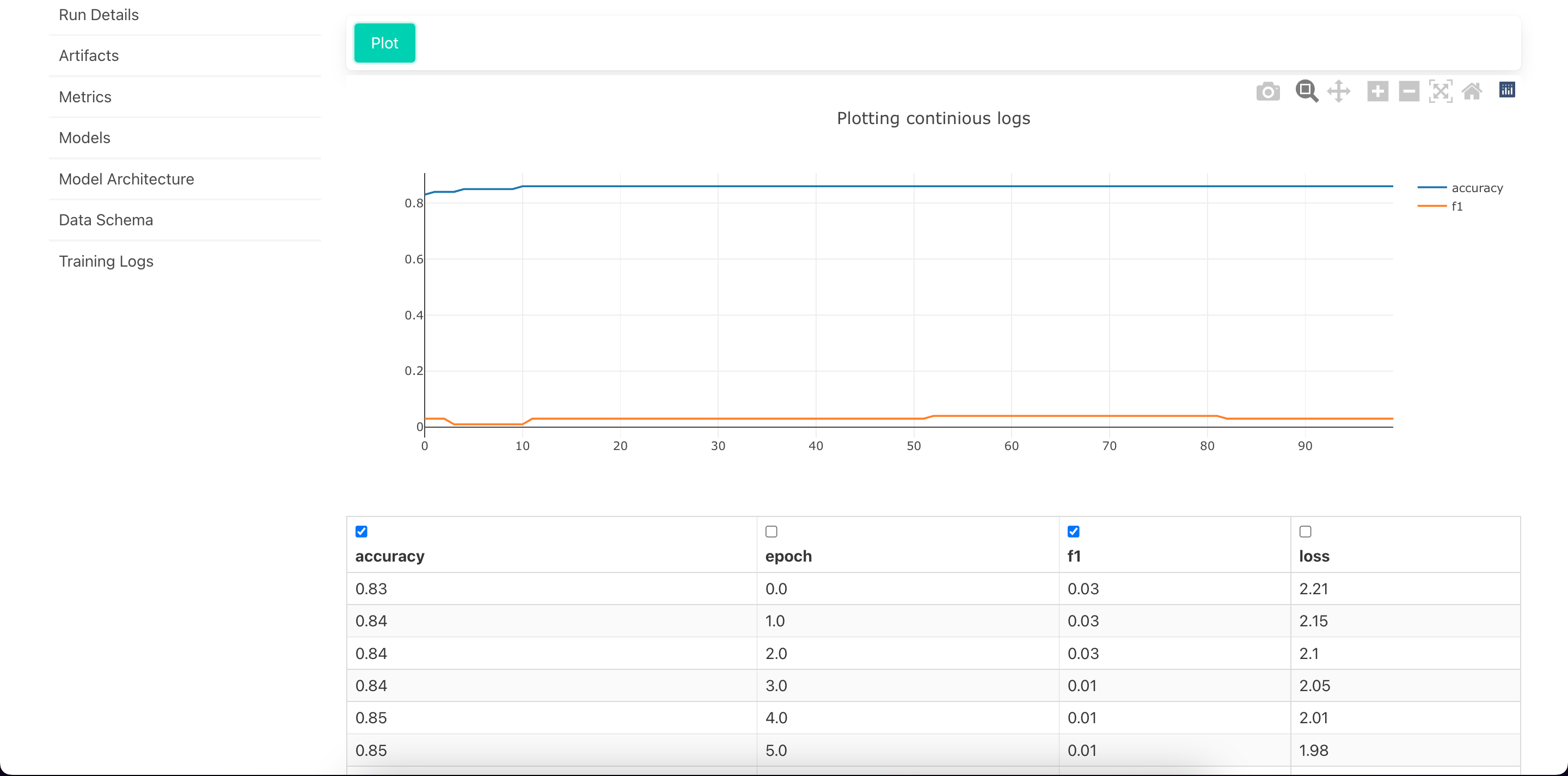
Visualize Training Logs
Sample input for prediction
GET REQUEST - to get info for the model
- info : Contains model information
- request_body: Sample post Request
{
"info": {
"experiment_id": "Pytorch",
"model_deployment_number": "51c186ddd125386c",
"model_mode": "non_runtime",
"model_type": "torch",
"model_url": "/predict/51c186ddd125386c",
"run_id": "3fffe458-9676-4bc7-a6c0-a3b4cf38e277",
"status": "running"
},
"request_body": {
"data": [
[
42.0,
120.0,
1.0,
0.0,
0.0,
0.0,
185.7,
133.0,
31.57,
235.1,
149.0,
19.98,
256.4,
78.0,
11.54,
16.9,
6.0,
4.56,
0.0
]
],
"dtype": "float"
}
}
For POST REQUEST
-data--> list: contains data rows for prediction supports both batch prediction and single instance ex: data --> [ [ 0,1,2,3],[3,4,56 ] ]
-dtype--> str: for type conversion converts the data into required data type tensor
{
"data": [
[
42.0,
120.0,
1.0,
0.0,
0.0,
0.0,
185.7,
133.0,
31.57,
235.1,
149.0,
19.98,
256.4,
78.0,
11.54,
16.9,
6.0,
4.56,
0.0
]
],
"dtype": "float"
}
Contributing
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.
